Parmesan cheese, also known as Parmigiano-Reggiano, is an Italian hard, granular cheese made from cow’s milk. It originated in Italy and is typically aged for at least 12 months, though some varieties can be aged up to 36 months or more. Parmesan cheese has a sharp, nutty flavour and a firm, gritty texture due to its ageing process.
Parmigiano-Reggiano is the original Italian cheese name for parmesan. Parmigiano-Reggiano is named after two Italian areas which produce it, the Italian provinces of Parma and Reggio Emilia. This type of cheese is also produced in Bologna west of the River Reno and Modena, located in the Emilia-Romagna region.
Top 12 Facts About Parmesan Cheese:
- Source of Milk: Cow milk
- Texture: Hard and granular
- Colour: Pale yellow
- Flavour: Nutty, savory, and slightly sharp
- Fat Content: 25-30%
- Aging Time: Aged for 12-36 months
- Pasteurized: Typically pasteurized
- Country of Origin: Italy
- Town: Produced in various Italian regions, notably Parma, Reggio Emilia, and Modena
- Named After: The region of Parma in Italy
- Certification: Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) as Parmigiano-Reggiano
- Uses: Ideal for grating over pasta, risottos, soups, and as a key ingredient in many Italian dishes
In this article, we’ll delve into the Production, History and origin, and health benefits of parmesan cheese:
How Parmesan Cheese is Made
The production of Parmesan or Parmigiano-Reggiano cheese is a meticulous process that contributes to its distinctive flavor and texture. Here’s a detailed look at how Parmesan Cheese is Made, start with the milk collection:
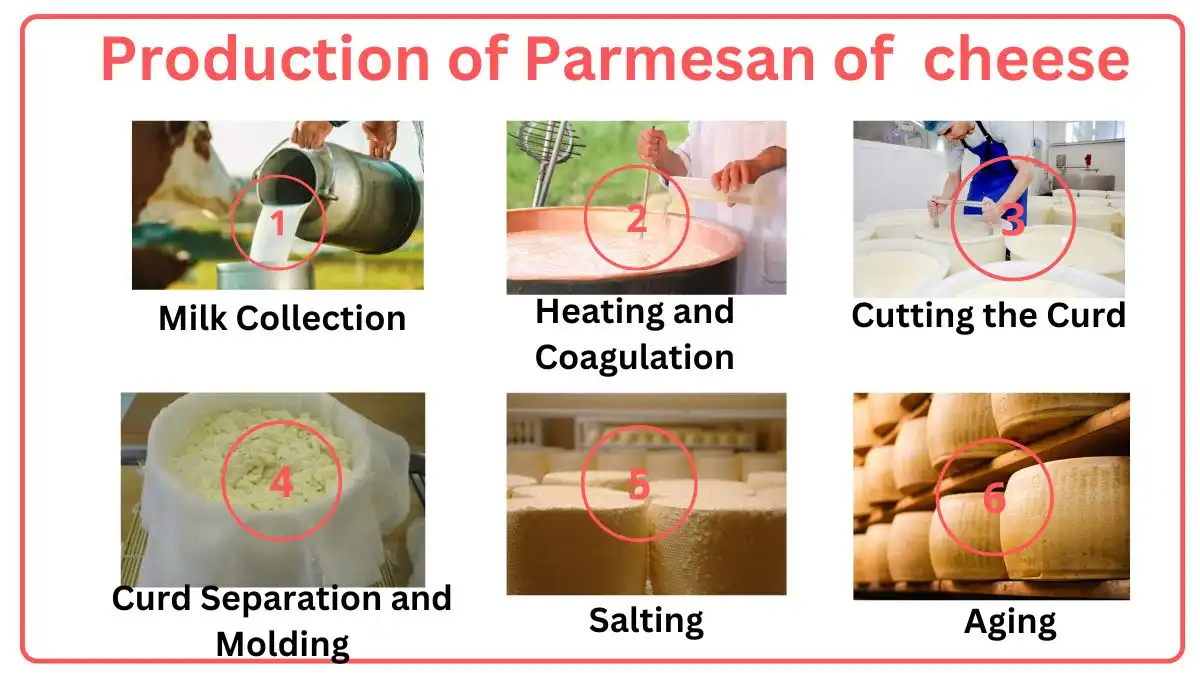
1. Milk Collection
The process begins with high-quality raw cow’s milk, sourced from cows that graze on fresh grass and hay in the Parma, Reggio Emilia, Modena, Bologna, and Mantua provinces of Italy. The milk is collected twice daily: the evening milk is left to sit overnight, allowing the cream to rise to the top, which is then skimmed off. The partially skimmed milk is mixed with the fresh morning milk, creating the perfect balance for cheese production.
2. Heating and Coagulation
The mixed milk is poured into large, copper cauldrons and gently heated to around 33-35°C (91-95°F). Natural whey starter, which is a byproduct from the previous day’s cheese-making process, is added to acidify the milk. Calf rennet is then introduced, causing the milk to coagulate and form curds. This step typically takes about 10-12 minutes.
3. Cutting the Curd
Once the curd has formed, it is cut into tiny granules using a special tool called a “spine.” The cutting process is crucial as it helps expel whey from the curd, ensuring the desired texture. The curds are then gradually heated to about 55°C (131°F) while being stirred continuously. This cooking process takes around 30-45 minutes, during which the curd granules shrink and firm up.
4. Curd Separation and Molding
After cooking, the curd granules settle at the bottom of the cauldron, forming a mass. The curd mass is then lifted using a muslin cloth and divided into two portions, each of which will become a wheel of Parmesan cheese. These portions are placed into round moulds, which give the cheese its characteristic shape. A unique casein plate with an identification code is inserted into each cheese, ensuring traceability.
5. Salting
The cheese wheels are immersed in a brine solution, typically made of water and salt, for about 20-25 days. This salting process enhances the flavour and helps in the preservation of the cheese. During this period, the cheese wheels are regularly turned to ensure even absorption of the salt.
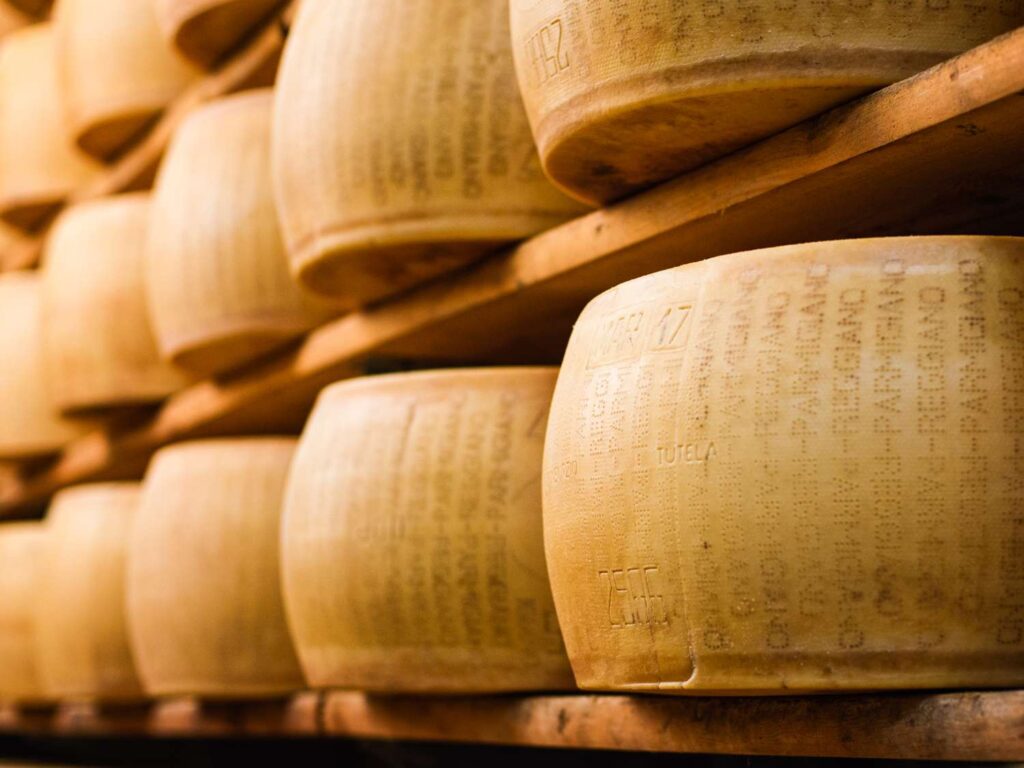

6. Aging
Ageing, or maturation, is the final and most critical step in the production of Parmesan cheese. The wheels are placed on wooden shelves in a temperature and humidity-controlled environment. They are turned and brushed regularly to prevent mould growth and ensure uniform ageing. The minimum ageing period for Parmesan cheese is 12 months, but some wheels are aged for 24, 36, or even 48 months. The longer the ageing period, the more complex and intense the flavour becomes.

7. Quality Inspection
Before the cheese can be sold as Parmigiano-Reggiano, it must pass a rigorous quality inspection conducted by the Consorzio del Formaggio Parmigiano-Reggiano. Inspectors use a small hammer to tap the cheese wheels, listening for any irregularities in the sound that might indicate defects. Wheels that meet the strict standards are branded with the Parmigiano-Reggiano mark.
Recommended Reading The Ultimate Guide to Cheddar Cheese
For more on Parmesan cheese, its origin, regulations, and authentic characteristics, visit the Parmesan Wikipedia page. This resource offers a detailed overview of how the cheese is protected within European and global markets.
History of Parmesan Cheese:
Parmesan cheese, or Parmigiano-Reggiano, is a product of tradition, craftsmanship, and centuries of culinary evolution. Its origins date back nearly a thousand years, and its history is intertwined with the culture and cuisine of Italy. Here’s an in-depth look at the history of Parmesan cheese.
Origins in Medieval Italy
The story of Parmesan cheese begins in the Middle Ages, around the 12th century, in the region of Emilia-Romagna in northern Italy. The cheese was first produced in the provinces of Parma, Reggio Emilia, Modena, and parts of Bologna and Mantua. The fertile plains and abundant pastures of these areas provided ideal conditions for dairy farming.
Parmesan derives from the Swiss cheese sbrinz. During the Middle Ages, sbrinz was transported to Italy from Switzerland across the Alps. The cheese was called spalenkäse at that time before taking the name of sbrinz in the 16th century. Swiss cheesemakers settled in Italy and gave birth to parmesan which is made using the same technique as sbrinz
Development and Spread
During the Renaissance, Parmesan cheese gained popularity among the Italian nobility and wealthy merchants. Its rich flavor and unique texture made it a favorite in the sophisticated kitchens of the time. Parmesan cheese was often gifted to dignitaries and featured in lavish feasts, further cementing its status as a prized delicacy.
The cheese’s fame began to spread beyond Italy’s borders. By the 14th and 15th centuries, Parmesan was being traded in markets across Europe. Historical records show that it was even mentioned in the writings of famous figures like Giovanni Boccaccio and Samuel Pepys, highlighting its esteemed reputation.
Recommended Reading The Service of cheese in restaurants
Why is Parmesan cheese so expensive?
Parmesan cheese, or Parmigiano-Reggiano, is renowned for its rich flavour, versatility, and high quality. Let’s explore the various factors that contribute to its cost.
1. Strict Production Standards
Parmesan cheese is produced according to rigorous standards set by the Consorzio del Formaggio Parmigiano-Reggiano. These standards ensure that only cheese made in specific regions of Italy, using traditional methods, can be labeled as Parmigiano-Reggiano. The adherence to these stringent guidelines guarantees the cheese’s authenticity and quality but also increases production costs.
2. High-Quality Raw Materials
The production of Parmesan cheese starts with high-quality raw cow’s milk from cows that graze on fresh grass and hay. The milk must come from specific breeds of cows in the designated regions. This emphasis on high-quality, locally sourced milk ensures the cheese’s superior taste and texture but adds to the cost.
3. Labor-Intensive Process
Making Parmesan cheese is a labour-intensive process that requires skilled artisans. From the initial coagulation of the milk to the precise cutting of the curds and the meticulous ageing process, each step demands expertise and attention to detail. The manual labour involved, combined with the need for experienced cheesemakers, contributes to the higher price.
4. Extended Aging Period
One of the key factors that set Parmesan cheese apart is its extended ageing period. The cheese must be aged for a minimum of 12 months, but many varieties are aged for 24, 36, or even 48 months. During this time, the cheese develops its characteristic flavour and texture. The long ageing process requires significant storage space and careful monitoring, both of which add to the production costs.
5. Limited Production Area
Parmesan cheese can only be produced in specific regions of Italy: Parma, Reggio Emilia, Modena, and parts of Bologna and Mantua. This limited production area restricts the quantity of cheese that can be produced, making it a relatively rare commodity. The geographic limitation contributes to its exclusivity and higher price.
6. Quality Control and Certification
Each wheel of Parmesan cheese undergoes rigorous quality control inspections by the Consorzio del Formaggio Parmigiano-Reggiano. Inspectors use specialized tools to check for defects and ensure the cheese meets the strict standards required for the Parmigiano-Reggiano designation. This thorough quality control process ensures a consistent, high-quality product but adds to the overall cost.
7. Import Costs and Tariffs
For consumers outside of Italy, additional costs are associated with importing Parmesan cheese. These costs include transportation, import tariffs, and distribution fees. As a result, the price of Parmesan cheese can be significantly higher in international markets compared to its cost in Italy.
8. Market Demand
Parmesan cheese is highly sought after for its unique flavor and versatility in cooking. The strong demand, combined with the limited supply, drives up the price. Consumers are willing to pay a premium for authentic Parmesan cheese, contributing to its higher market value.
Recommended: 27 different types of cheese: their origin and uses
Uses of Parmesan Cheese
This hard, granular cheese is a staple in many kitchens, adding depth and umami to a variety of dishes. Let us explore how the cheese could be used:

1. Grated Over Pasta
One of the most popular uses of Parmesan cheese is grating it over pasta. The cheese melts beautifully, adding a rich, savoury flavour to your favourite pasta dishes. Whether it’s a simple spaghetti aglio e olio or a hearty lasagna, a sprinkle of Parmesan cheese can elevate the dish to new heights.
2. In Soups
Adding grated Parmesan cheese to soups can enhance their flavour and add a creamy texture. Try stirring some into minestrone, tomato soup, or any vegetable-based soup for a delicious twist.
3. In Risottos
Parmesan cheese is a key ingredient in many risotto recipes. It adds creaminess and depth of flavour to the dish. A classic Parmesan risotto or a mushroom risotto with Parmesan is sure to impress your guests.
Innovative Uses of Parmesan Cheese
1. Parmesan Crisps
Parmesan crisps, or frico, are a delightful snack or garnish. Simply grate Parmesan cheese onto a baking sheet and bake until golden and crispy. These crisps are perfect for adding a crunchy element to salads or soups, or for enjoying on their own as a snack.
2. In Salads
Shaved Parmesan cheese adds a gourmet touch to salads. It pairs beautifully with fresh greens, nuts, and vinaigrette. Try it in a classic Caesar salad or a mixed green salad with balsamic dressing.
3. As a Crust for Meats and Fish
Creating a Parmesan crust for meats or fish adds a flavorful and crispy coating. Mix grated Parmesan cheese with breadcrumbs and herbs, then coat chicken, pork, or fish before baking or frying. This method gives your dishes a delicious, cheesy crust.
ALSO READ: Discovering The Cottage Cheese
Health benefits of Parmesan cheese:
Parmesan cheese can be a valuable component of a balanced diet. In this article, we’ll explore the many health benefits of Parmesan cheese and why you should consider incorporating it into your meals.
1. High in Protein
Parmesan cheese is an excellent source of protein, which is essential for muscle building, tissue repair, and overall body function. Just one ounce of Parmesan contains around 10 grams of protein, making it a great option for those looking to increase their protein intake.
2. Rich in Calcium
Calcium is crucial for maintaining healthy bones and teeth, and Parmesan cheese is packed with this vital mineral. A single ounce of Parmesan provides about 30% of the recommended daily intake of calcium, supporting bone density and reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
3. Packed with Vitamins and Minerals
In addition to calcium and protein, Parmesan cheese is rich in several other important nutrients, including:
- Vitamin A: Essential for eye health, immune function, and skin health.
- Vitamin B12: Important for nerve function and the production of red blood cells.
- Phosphorus: Works with calcium to maintain strong bones and teeth.
- Zinc: Supports immune function and aids in wound healing.
Easy to Digest
One of the unique benefits of Parmesan cheese is that it is easier to digest than many other cheeses. This is because Parmesan is naturally low in lactose, the sugar found in milk that can cause digestive issues for some people. The ageing process of Parmesan cheese breaks down lactose, making it a suitable option for those who are lactose intolerant.
Supports Digestive Health
Parmesan cheese contains beneficial bacteria that promote gut health. These probiotics help balance the gut microbiome, aiding digestion and improving overall gastrointestinal function. Including Parmesan in your diet can contribute to a healthier digestive system.
Also Read: The Ultimate Guide to Bel Paese Cheese
BBC Good Food – for recipe inspiration featuring Parmesan cheese.
FAQ
What is Parmesan cheese?
Parmesan cheese, or Parmigiano-Reggiano, is a hard, granular cheese from Italy, known for its rich, nutty flavor and crystalline texture. It is often used as a grating cheese for various dishes.
What are the key differences between Parmesan and Parmigiano-Reggiano?
While “Parmesan” can refer to any cheese that resembles Parmigiano-Reggiano, true Parmigiano-Reggiano must be produced in specific regions of Italy and adhere to strict quality standards set by the Italian government.
How is Parmesan cheese made?
Parmesan cheese is made from cow’s milk, and its production involves a lengthy aging process, typically lasting at least 12 months. The cheese is cooked and pressed, resulting in its distinctive texture and flavor.
What are some common uses for Parmesan cheese?
Parmesan cheese is widely used in cooking and can be grated over pasta, added to risottos, incorporated into sauces, or enjoyed on its own as part of a cheese board. It pairs well with various foods, enhancing flavors and adding depth.
More on Cheese
- The Ultimate Guide to Cheddar Cheese
- Mozzarella cheese | Origins, Production, uses
- The Ultimate Guide to Ricotta Cheese
- Homemade Ricotta Cheese Recipe
- Complete guide to Feta cheese
- Discovering The Cottage Cheese
- The Ultimate Guide to Danish Blue Cheese
- The Ultimate Guide to Bel Paese Cheese
- Cream Cheese Essentials: Everything You Need to Know
- Camembert Cheese: A Comprehensive Guide
- 27 different types of cheese: their origin and uses
- Service of cheese in restaurants
Subscribe and join our community of hospitality professionals & students — get insights, tips, and the latest updates delivered straight to your inbox!







